Excel COUNTIF Function
COUNTIF Function
The COUNTIF function is a premade function in Excel, which counts cells as specified.
It is typed =COUNTIF
NOTE: The COUNTIF function can have basic or more advanced uses. This covers the basic use for how to count specific numbers and words.
Numbers (e.g. 90) and words (e.g. "Water") can be specified.
How to use the =COUNTIF function:
- Select a cell
- Type
=COUNTIF - Double click the COUNTIF command
- Select a range
- Type
, - Select a cell (the criteria, the value that you want to count)
- Hit enter
Note: The different parts of the function are separated by a symbol, like comma , or semicolon ;
The symbol depends on your Language Settings.
Let's see some examples!
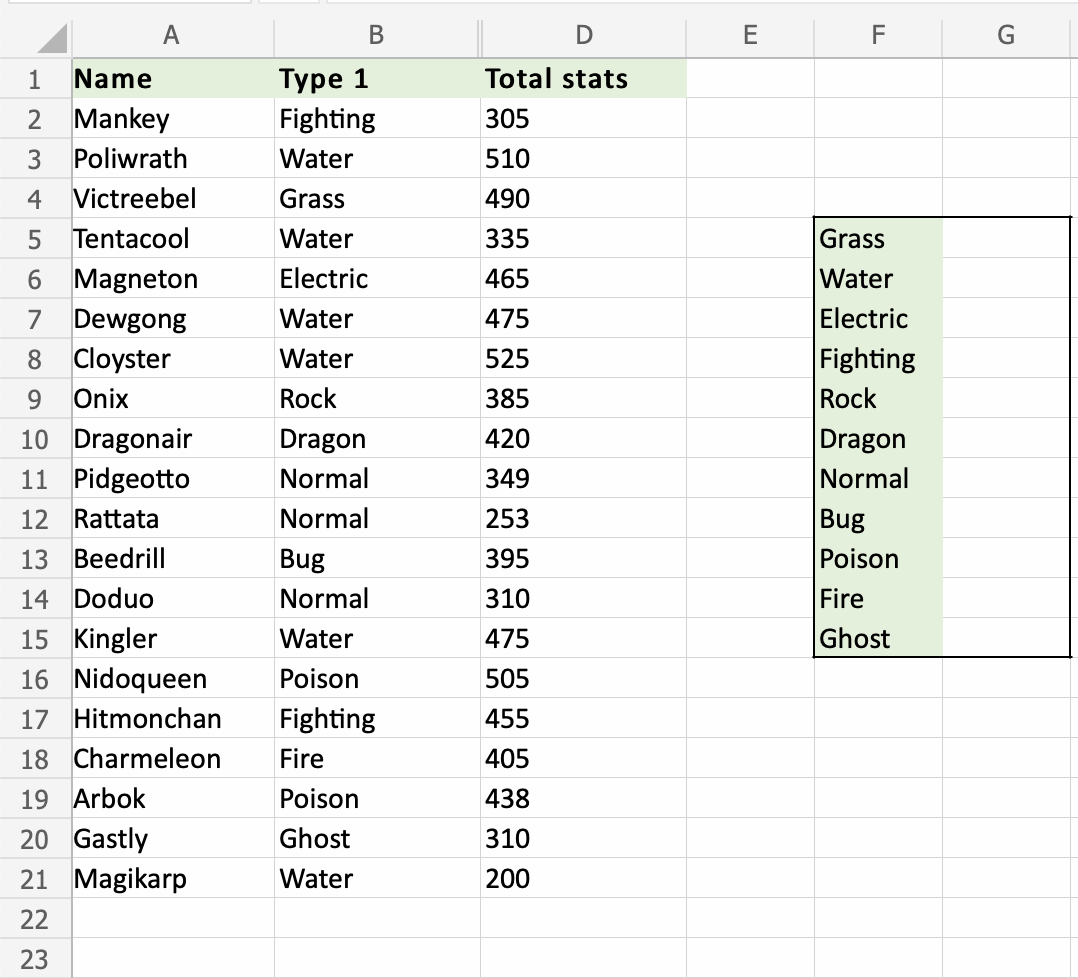
Apply the COUNTIF function to range B2:B21, to count how many Pokemons we have in the different types:
We want the COUNTIF function to count the types of Pokemons, in the range G5:G15:
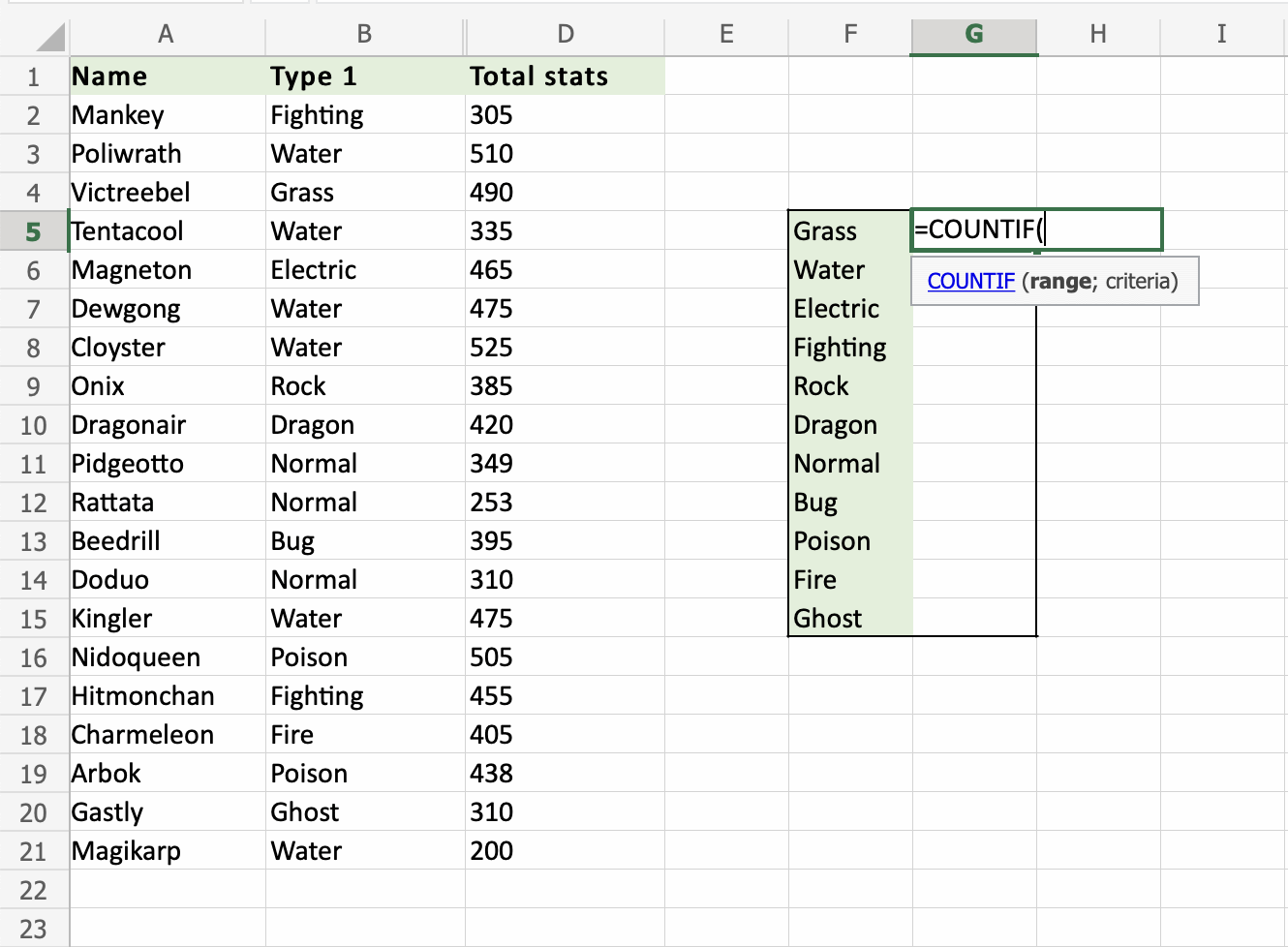

The , is typed after the range is selected, which tells the function what you are looking to count.

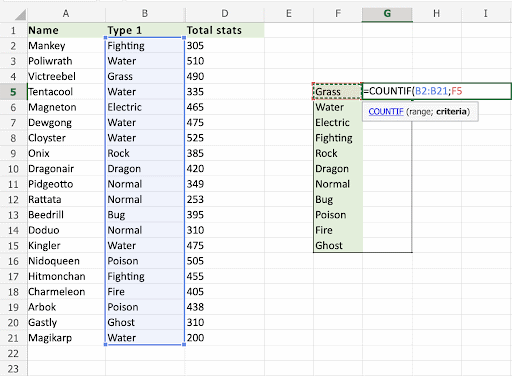

The COUNTIF function has successfully counted 1 Grass Pokemon, which is Victreebel (A4).
Let's count the Water Pokemons in G6
The same steps apply
- Select
G6 - Type
=COUNTIF - Select
B2:B21 - Type (
,) - Select
F6(Specifying Water as criteria) - Hit enter
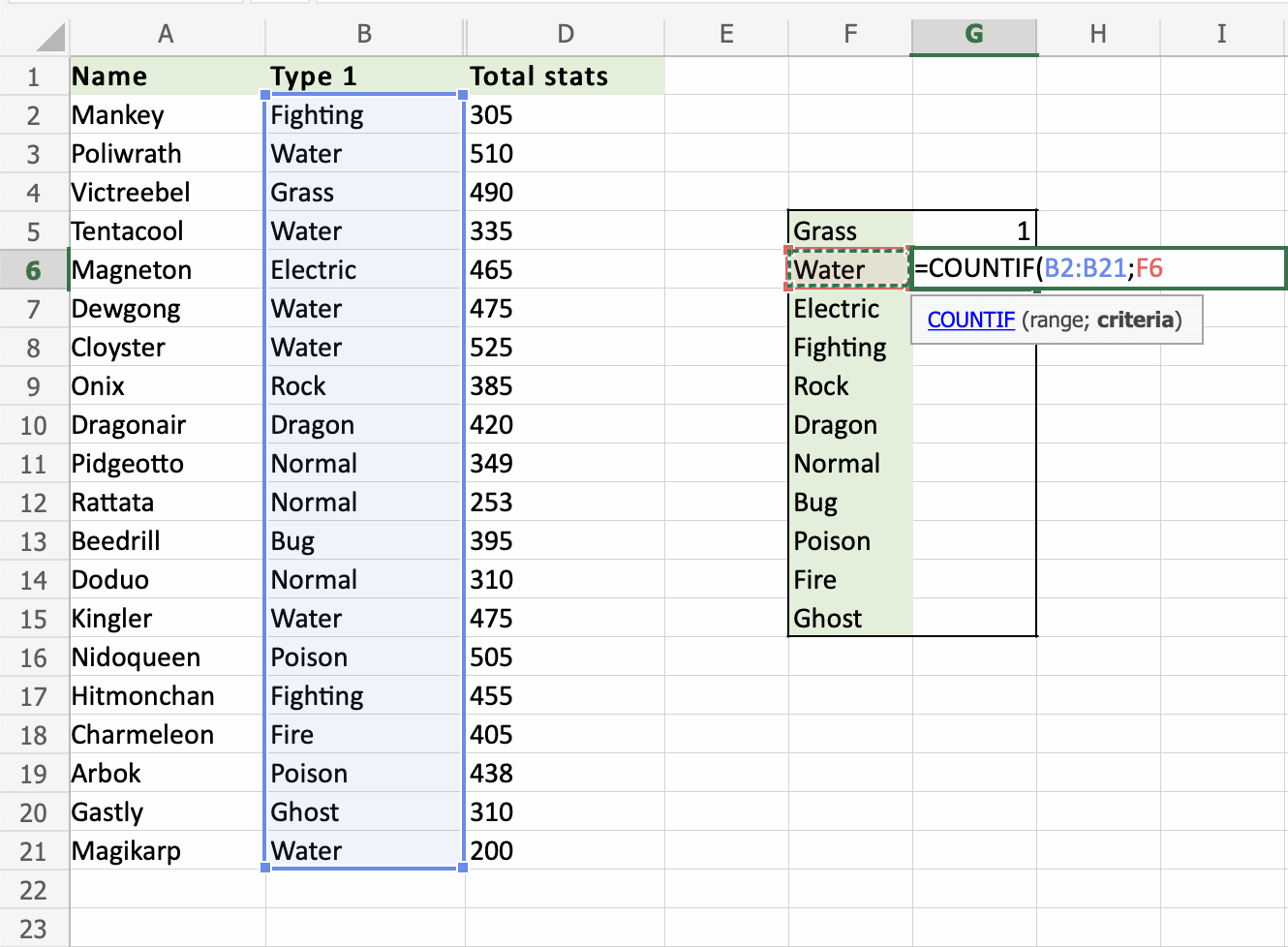
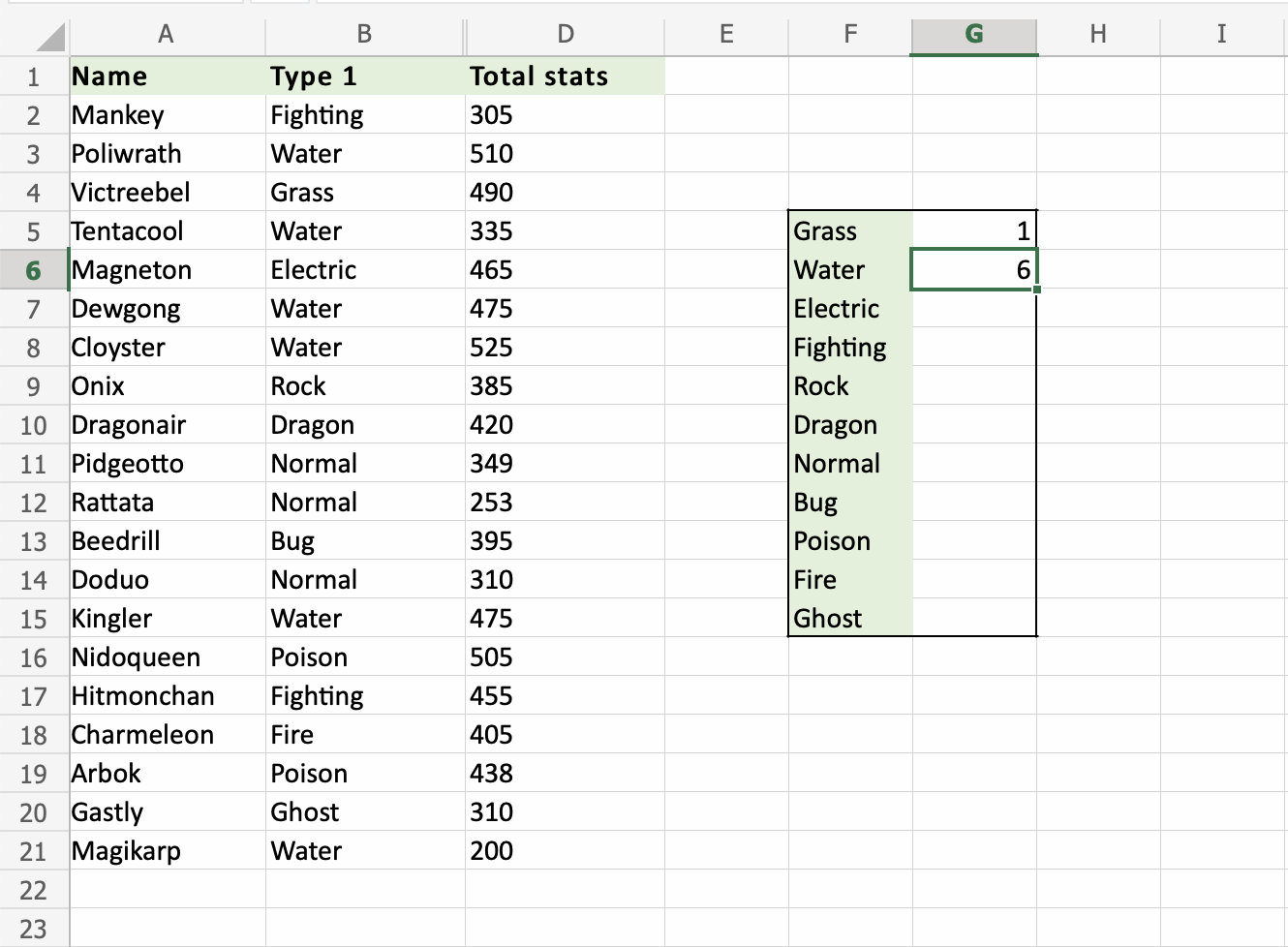
That is great! The COUNTIF function has counted 6 Water Pokemons in B2:B21.
Let's count the rest of the types more effectively. We want to continue the function from G6:G15. Making use of the Filling Function and Absolute References.
Step by step:
- Double click
G6 - Lock the range references absolute (
B2:B21). Type dollar signs before the columns and row. Type 4 dollar signs in total.=COUNTIF($B$2:$B$21,F6). Note: We wantF6to remain relative. Because we want it to move downwards. Do not add dollar signs ($) to it. - Hit enter
- Fill the range
G6:G15
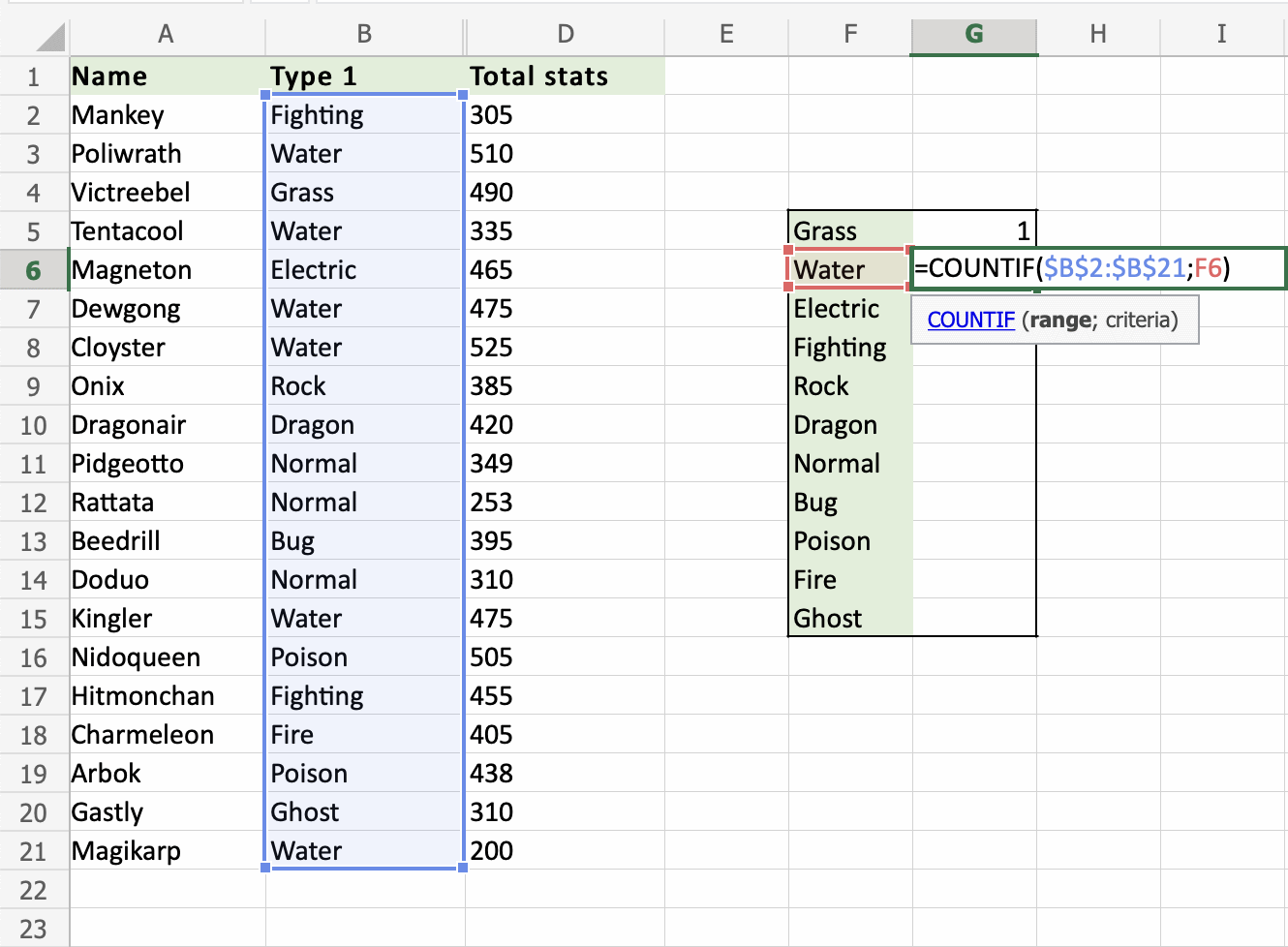
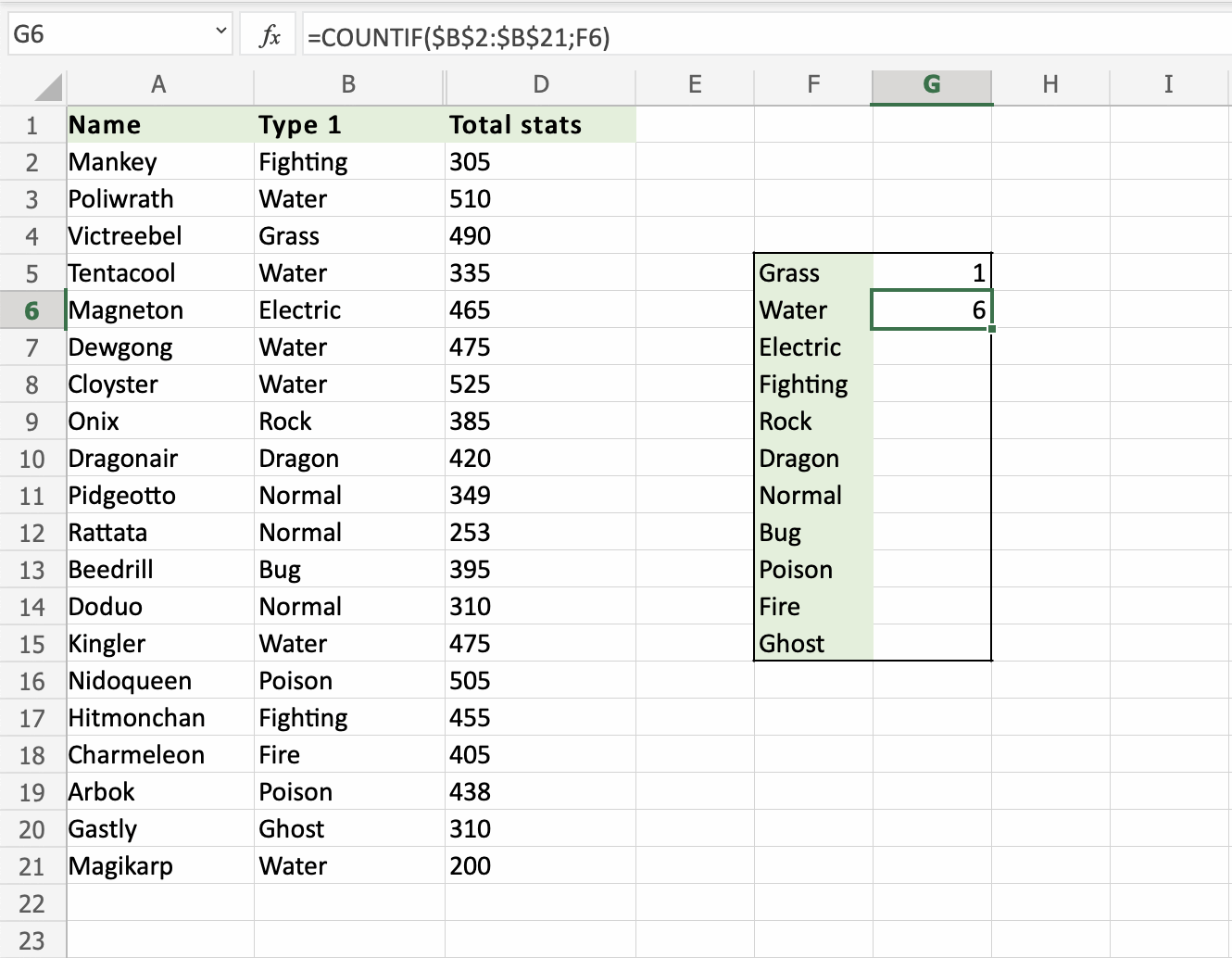
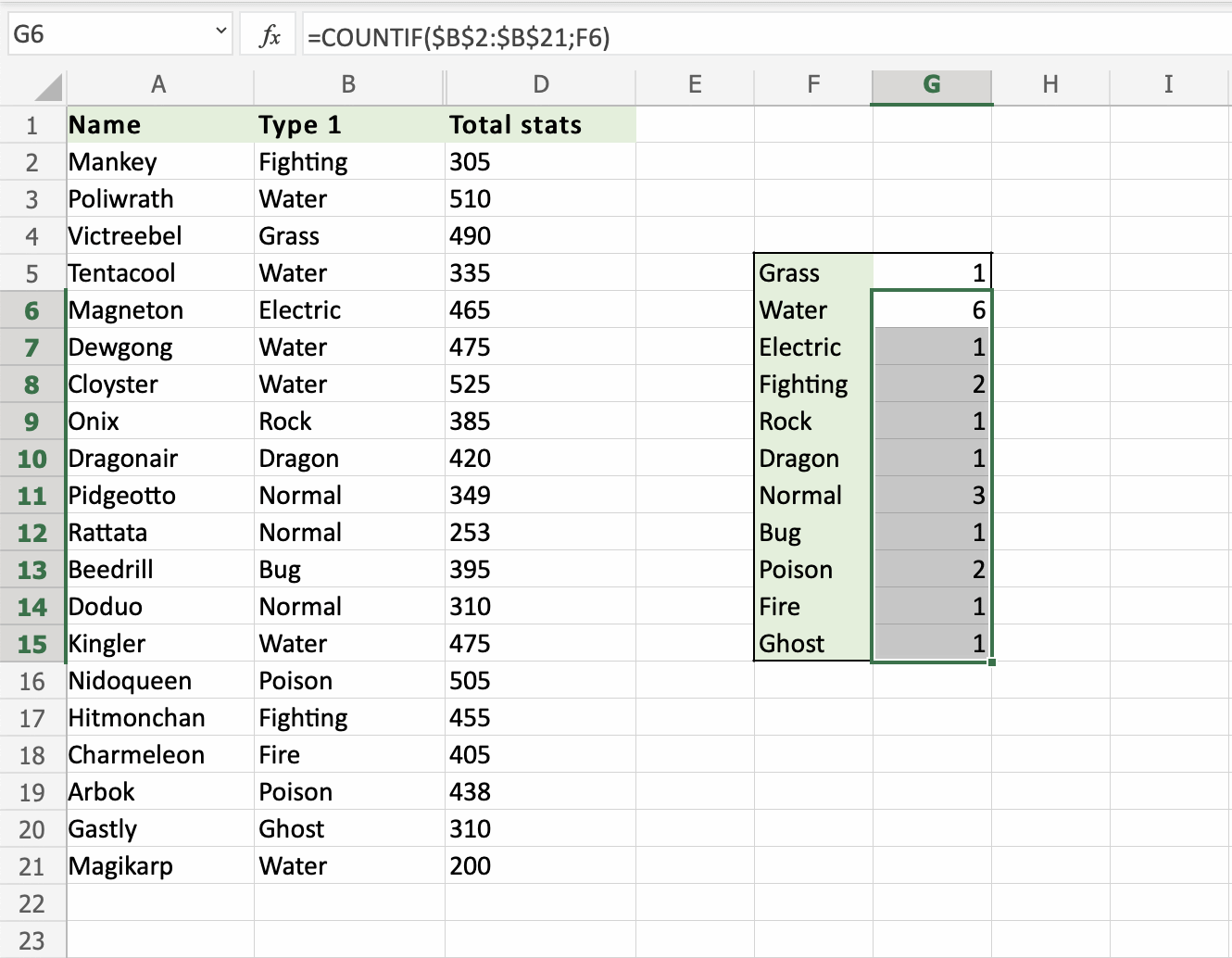
That saved us alot of time! Good job!
A Non-Working Example
Let's try an example that will not work
Fill G5:G15 without locking the references to see what happens.

If the references for the range are kept relative, the fill function will move the range downwards, including blank cells and missing the range where the data is.